__GROUP 7 - THE HALOGENS__
Halogens are nonmetallic elements with 7 valence electrons. The term 'halogen' originated from the Greek words "hal"(salt) and "gen"(to produce), because because they all produce salts of similar properties.
Halogens form diatomic molecules; in other words, 'two atom' molecules.

The yellow part in the periodic table is the Halogens group.
ELEMENTS IN THE HALOGEN GROUP
F-Fluorine
Cl-Chlorine
Br-Bromine
I-Iodine
At-Astatine
The halogens exist, at room temperature, in all three states of matter:
Solid-> Iodine, Astatine
Liquid-> Bromine
Gas-> Fluorine, Chlorine
PICTURES OF HALOGENS LINK
Click below
http://isbchem1.pbwiki.com/f/PicturesofHalogens.doc
http://www.webelements.com/webelements/elements/text/F/econ.html
__PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF HALOGENS__
Trends in Melting Point and Boiling Point

As you can see on the graph above, the boiling point and the melting point both rise as you go down the group.
DENSITY at 293K:
F: 1.696 g/cm3
Cl: 3.214 g/cm3
Br: 3.119 g/cm3
I: 4.93 g/cm3
At: Unknown
MELTING POINTS:
F: -219.62 °C
Cl: -100.98 °C
Br: -7.2 °C
I: 113.5 °C
At: 302.0 °C
BOILING POINTS:
F: -188.14 °C
Cl: -34.6 °C
Br: 58.78 °C
I: 184.0 °C
At: 337.0 °C
__CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF HALOGENS__
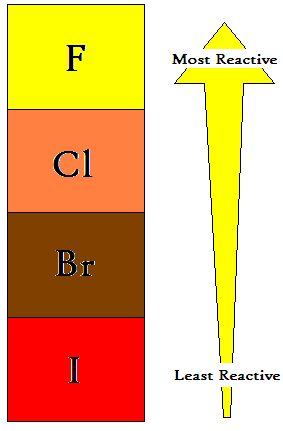
The halogens get less reactive as you go down the group.
ELECTRON CONFIGURATION:
F- 2,7
Cl- 2,8,7
Br- 2,8,18,7
I- 2,8,18,18,7
At- 2,8,18,32,18,7

COMPOUNDS AND THEIR USES
Fluorine
• Most reactive of all non-metals (reacts even with glass)
• Forms useful compounds like Teflon, used to create non-stick surfaces and coat certain types of bullets. However, the use of Teflon coating in kitchenware is now heavily debated because the coating can release extremely harmful gases when temperatures exceed 660°F. (New tests have shown that Teflon coated cookware exceeded that temperature and turned toxic through the common act of preheating a pan, on a burner set on high)
• Often used in toothpaste to prevent tooth decay (fluoride forms part of the calcium compounds in your teeth making it harder for acid to attack teeth.
• Sometimes added to water supply though too much fluoride is poisonous and can be fatal

Chlorine
• Most common compound is sodium chloride, or table salt!
• Found and produced in every human’s body as HCL (Hydrochloric Acid)
• Found in bleach to kill bacteria and whiten
• Used to kill bacteria in:
o Swimming pools
o Drinking water
o Antiseptics and disinfectants

Bromine
• Used primarily in pesticides
• Sometimes used in medicines
• Silver bromide is used in photographic film
Iodine
• Often used as antiseptic
• Silver iodide is used in photographic film
• It can also be used as a nutrient
Astatine
• Radioactive therefore no real-world uses aside from scientific research
• Due to its scarcity, astatine is produced when it is needed
OTHER LINKS:
http://www.chemicalelements.com/groups/halogens.html
http://www.chemsoc.org/viselements/Pages/data/intro_groupvii_data.html
http://www.chemguide.co.uk/inorganic/group7/properties.html
Displacement
Reaction of gaining more electrons.
Halogen with higher reactivity displaces with the one with lower reactivity.
chlorine + sodium bromide � sodium chloride + bromine
Cl2(aq) + 2NaBr(aq) � 2NaCl(aq) + Br2(aq)
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.