Halogens

The highlighted area is where the halogens are found on the periodic table
Image from http://www.chem4kids.com/files/elem_halogen.html
The term halogen means an element that forms salt when bonded with another metal. Halogens are found in Group 7. That means that they are require only one more electron to obtain a full valence shell. Thanks to this trait, they bond to myriad different molecules, but are most commonly found bonding either to:
- Each other (as they are diatomic molecules)
- To molecules found in Group 1, which only have one extra electron.
General Halogen Information
| Halogen Molecule | Colour | State of Matter (at room temp.) | Melting Temp. (°C) | Boiling Temp. (°C) | Electron Configuration | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass |
| Fluorine | pale yellow | gas | -219.62 °C | -188.14 °C | 2,7 | 9 | 19 |
| Chlorine | yellow-green | gas | -100.98 °C | -34.6 °C | 2,8,7 | 17 | 35 |
| Bromine | orange-brown | liquid | -7.2 °C | 58.78 °C | 2,8,18,7 | 35 | 80 |
| Iodine | grey-black | solid | 113.5 °C | 184.0 °C | 2,8,18,32,18,7 | 53 | 127 |
Atomic Structure
 <-- Flourine
<-- Flourine  <-- chlorine
<-- chlorine
 <-- Bromine
<-- Bromine  <-- Iodine
<-- Iodine
Halogens are...
- Five non-metal elements
- Found in group 17 of the Periodic Table
- “Salt-former” : compounds containing halogens are called “salts”
- 7 electrons in their outer shells
- Exist in all three states of matter at room temperature.
- Diatomic elements
Physical Properties
Halogens, on their own, tend to form as diatomic molecules. The melting points, boiling points, and atomic radii all increase as you move down the group, but their reactivity with other elements increase as you move upwards.
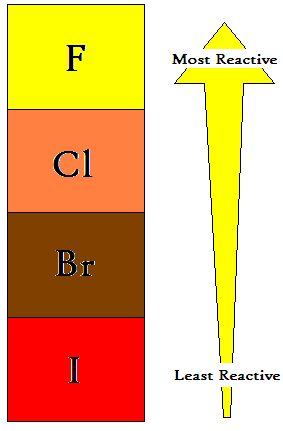
- Found on the second column from the right
- Having Bad, Strong odor
- Cause painful burns from skin contact
- Harming mucous membranes
- Soluble in water
- Going down the periodic table, have high melting/boiling points
(Fluorine having the lowest and Iodine having the highest ones)
- Going down the periodic table, the halogens get denser, and the reactiveness becomes lower
- All of halogens except iodine are poisonous
- Found in each of the different states of matter
(Fluorine, Chlorine: gas / Bromine: liquid / Iodine: Solid)
Chemical Properties
Halogens are known as the most reactive of non-metallic substances. Fluorine is the most reactive, oxidizing, and acidic of halogens, followed by chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
A halogen that has bonded and fromed a compound is called a halide. An example of a halide is sodium chloride (NaCl), or common table salt. When a halide is formed, the halogen that is part of the halide, for example, chlorine in sodium chloride, ends with an -ide. When bonded with another element, fluorine becomes fluoride, bromine becomes bromide, and iodine becomes iodide
- Halogens contain seven valence electrons
- Exist as diatomic molecules in room temp.
- Bond with elements from group one
(Alkali Metals have one valence electrons)
Other Facts
Fluorine is found in:


Chlorine is found in:
- Swimming pools
- Salt
- Bleach
- Disinfectants
- Drinking water


Bromine is found in:
- Antiseptics and disinfectants
- Silver bromide is used in photographic film
Iodine is found in:
- Antiseptics
- Special dyes
- First aid
- Seaweed
__To get more detailed information about Fluorine, Bromine and Iodine, http://isbchem1.pbwiki.com/f/FBI.ppt < click here to see the powerpoint presentation. (Chlorine is coming up!)__
Use of halogens
Fluorine: Fluorine is the most reactive of the halogens. Alone it is poisonous, but in compounds, its characteristics are completely different. Many types of toothpaste contain fluorine to prevent tooth decay, and some water supplies have fluorine added to them for the same reason. Fluorine is also commonly used bonded to Carbon, as Teflon.
Chlorine: Chlorine has many more uses than Fluorine. Chlorine is most commonly found bonded to sodium, as sodium chloride, or more commonly known as salt. Chloride is also used to kill bacteria in swimming pools and drinking water. It is used to bleach paper and in disinfectants. Chloride is also found in many pesticides and weed killers.
Bromine: Bromine is also used in pesticides. It is also a compound in some medicines, and silver bromide is used in photographic film.
Iodine: Iodine is the least reactive of the halogens. Because it is an antiseptic, it is mainly found in disinfectants, diluted with alcohol.
Detriments of Halogens:
- Chlorine was used as the first even chemical weapon, and is still used in biological nerve gas.
- While chlorine kills bacteria in drinking water, it is not 100% effective and becomes poisonous in high doses.
- Halogen-based pesticides potentionally affect wildlife, whether directly or indirectly, and purposefully or accidentally.
- Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, is a very widely used but toxic plastic. When set on fire, hydrochloric acid is released.
- Chloro-fluro-carbon, or CFC, is a widely used coolant and is also found in aerosols. Unfortunately, it is primarily responsible for Earth's rapidly deteriorating ozone layer, which shields us from the full brunt of the Sun's UV rays.
Note
Astatine, which is also a halogen, was not covered in this wiki because it is considered a semi-metal. For more information on Astatine, please visit the semi-metal page. :D
note outline:
http://isbchem1.pbwiki.com/f/The%20halogens%20note%20outline.doc
Sources:
http://www.chemsoc.org/viselements/Pages/data/intro_groupvii_data.html
Chemistry for You by Lawrie Ryan
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.